Mouth cancer, or oral cancer, has become an increasingly prevalent health issue worldwide. While various factors contribute to its rise, habits such as smoking and chewing tobacco stand out as major culprits. The gravity of this condition cannot be overstated, as it affects several parts of the mouth, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, gums, and even the throat’s lower part.
The Rising Concern of Mouth Cancer
This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures of mouth cancer, with a particular focus on the impact of chewing tobacco. Additionally, we’ll explore why gum bleeding can occur even in the absence of smoking or tobacco use and discuss the treatment options available. Throughout, we’ll ensure that the content maintains a good balance of complexity and variation, in line with the concepts of perplexity and burstiness.
What Are the Symptoms of Mouth Cancer from Chewing Tobacco?
Chewing tobacco is often perceived as a safer alternative to smoking. However, this misconception can lead to severe consequences, including the development of mouth cancer. The symptoms of mouth cancer from chewing tobacco are often subtle at first but become increasingly apparent as the disease progresses.
Painless Swelling and Lumps
One of the early signs of mouth cancer is the presence of painless swelling or lumps inside the mouth. These masses may start small but tend to grow over time. If you notice a persistent lump or swelling that doesn’t go away, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional immediately. This could be an early indication of cancer developing in the mouth.
Difficulty in Tongue Movement and Speech
Another symptom to be wary of is difficulty moving the tongue or problems with speech. Cancerous growths can restrict tongue movement, making it challenging to speak or eat. If you experience severe pain while yawning or opening your mouth, it’s essential not to ignore these signs.
Persistent Throat Pain
Throat pain that doesn’t subside, even after recovering from a cold or viral infection, can be a red flag. While temporary throat discomfort is common, prolonged pain that lingers may suggest something more serious, such as oral cancer.
White or Red Patches in the Mouth
The appearance of white or red patches inside the mouth is another symptom associated with mouth cancer. Individuals who regularly consume tobacco products should be especially vigilant about these signs. Leukoplakia, characterized by white patches, is often an early indicator of cancer.
Visible Swelling on the Cheeks or Throat
Sometimes, mouth cancer can manifest as visible swelling on the cheeks or throat, which might not be painful initially. However, any unusual growths or lumps that appear should be evaluated by a doctor to rule out cancer.
How Long Does It Take to Get Cancer from Chewing Tobacco?
The timeline for developing cancer from chewing tobacco varies depending on several factors, including the frequency and duration of tobacco use. Some individuals may develop cancer after just a few years of use, while others might not see symptoms for decades. However, the risk increases significantly with prolonged use.
Understanding the Risk
Chewing tobacco exposes the mucous membranes in the mouth to harmful carcinogens. Over time, these substances cause changes in the cells lining the mouth, leading to the development of squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. The longer tobacco is used, the higher the risk of these cancerous changes occurring.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is key to successfully treating mouth cancer. Regular dental check-ups and self-examinations can help identify suspicious lesions or growths early on. If you use tobacco products, it’s crucial to monitor your oral health closely and seek medical advice if you notice any changes.
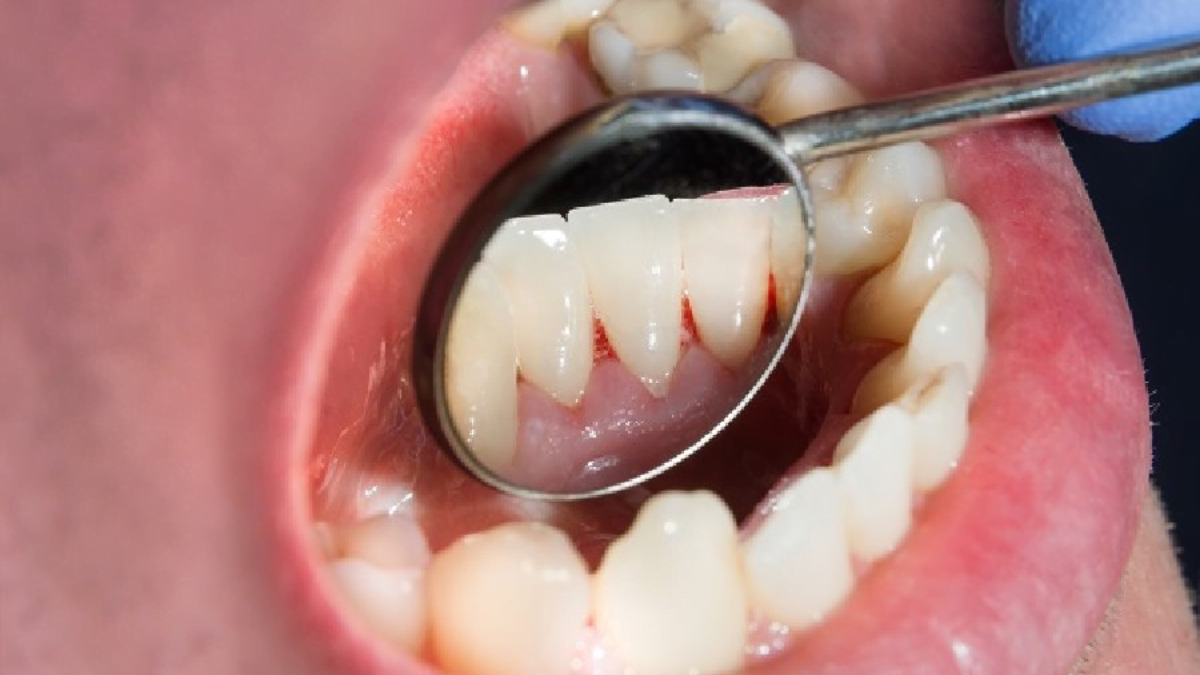
Do Not Smoke, Do Not Chew Tobacco! But the Gums Are Bleeding! Why?

It’s a common misconception that gum bleeding only occurs in individuals who smoke or use tobacco. However, gum bleeding can happen for various reasons, even in non-smokers and non-tobacco users.
Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the leading causes of gum bleeding is poor oral hygiene. Failing to brush and floss regularly can lead to the buildup of plaque, which irritates the gums and causes them to bleed. This condition, known as gingivitis, can progress to more severe forms of gum disease if left untreated.
Vitamin Deficiency
A deficiency in essential vitamins, particularly Vitamin C and Vitamin K, can also result in gum bleeding. These vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining healthy gums and blood clotting. A diet lacking in these nutrients can weaken the gums, making them more prone to bleeding.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy, can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding. This condition, known as pregnancy gingivitis, is usually temporary but requires proper oral care to prevent complications.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and blood disorders, can increase the risk of gum bleeding. Additionally, medications that thin the blood or affect clotting can also contribute to this issue.
The Importance of Professional Care
Regardless of the cause, it’s important to address gum bleeding promptly. Regular dental visits and maintaining good oral hygiene can prevent further complications and ensure your gums remain healthy.
Treatment Options for Mouth Cancer

If diagnosed early, mouth cancer is highly treatable. The treatment approach depends on the cancer’s stage, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is often the first line of treatment for mouth cancer. In some cases, this may involve removing part of the tongue, jaw, or other affected areas. The goal is to eliminate the cancerous cells while preserving as much function and appearance as possible.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. This treatment is often used in conjunction with surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. For early-stage cancers, radiation therapy alone may be sufficient.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It is typically used for more advanced stages of mouth cancer or when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy may be combined with radiation therapy to enhance its effectiveness.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances to specifically target cancer cells without harming normal cells. This type of treatment is often used for cancers that have specific genetic mutations.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation is a crucial aspect of the recovery process. Depending on the treatment received, patients may need therapy to regain speech and swallowing functions. Psychological support is also essential, as the diagnosis and treatment of cancer can be emotionally challenging.
Why Are Men More Affected by Mouth Cancer Than Women?

Mouth cancer is more common in men than women, and several factors contribute to this disparity.
Higher Rates of Tobacco and Alcohol Use
Men are more likely to use tobacco and consume alcohol, both of which are significant risk factors for mouth cancer. The combination of smoking and heavy drinking dramatically increases the likelihood of developing this type of cancer.
Occupational Hazards
Certain occupations, such as those involving exposure to chemicals or carcinogens, may increase the risk of mouth cancer. Men are more likely to work in these high-risk jobs, contributing to their higher incidence of the disease.
Delayed Diagnosis
Men may be less likely to seek medical attention for symptoms, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Early detection is critical for successful treatment, and delays can result in more advanced and harder-to-treat cancers.
The Global Increase in Mouth Cancer Cases
The number of cancer patients, particularly those with mouth cancer, is on the rise globally. Lifestyle factors, including tobacco use and poor oral hygiene, are significant contributors to this trend.
The Role of Tobacco Products
Tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, and smokeless tobacco, are major risk factors for mouth cancer. The carcinogens in tobacco damage the cells in the mouth, leading to mutations that can develop into cancer.
The Impact of Diet and Nutrition

A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants, can increase the risk of cancer. These foods help protect cells from damage, and their absence can make the body more susceptible to cancer.
The Need for Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about the risks of mouth cancer and the importance of early detection is essential. Education campaigns that promote regular dental check-ups and discourage tobacco use can play a significant role in reducing the incidence of mouth cancer.
Conclusion
Mouth cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, but it is also one that can often be prevented or treated successfully if detected early. Understanding the symptoms, risks, and treatment options is crucial for anyone who uses tobacco or is at risk for this disease.
By maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding tobacco products, and seeking regular medical care, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing mouth cancer.
Discover more from currentnewschannel.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.